CAVE: Collaborative Audio/Video Editor 🎬
Introduction
In my senior design course at MSU, formally known as The Capstone Experience, I had the opportunity to collaborate with five other students on a semester-long project to build and deliver a software application for a corporate client.
Our team, Team Techsmith, was sponsored by TechSmith corporation; headquartered in East Lansing, MI, TechSmith is a leading provider of screen capture software and offers products that are used by 73 million people worldwide and by every Fortune 500 company. In accordance with our client’s proposal, our team was tasked with developing the TechSmith Collaborative Audio/Video Editor (CAVE).
Collaborating with a team to create content is often challenging and restrictive to the creative workflow necessary when creating digitial media. CAVE is a web application that streamlines collaboration on media projects by enabling users to edit synchronously (think Google Docs but for media editing).
Users upload video, image, and audio files and arrange them with an intuitive timeline UI. Editors then preview the edited video at any time, and when completed, the final video can be downloaded for distribution across various platforms.
All media projects and their associated media are stored securely in the cloud where users can invite others to collaborate. Collaborators log in securely and can begin working on their project independently or together in real time.
This model of seamless collaboration enables the contribution of each team member to be better highlighted in the final product.
Demo
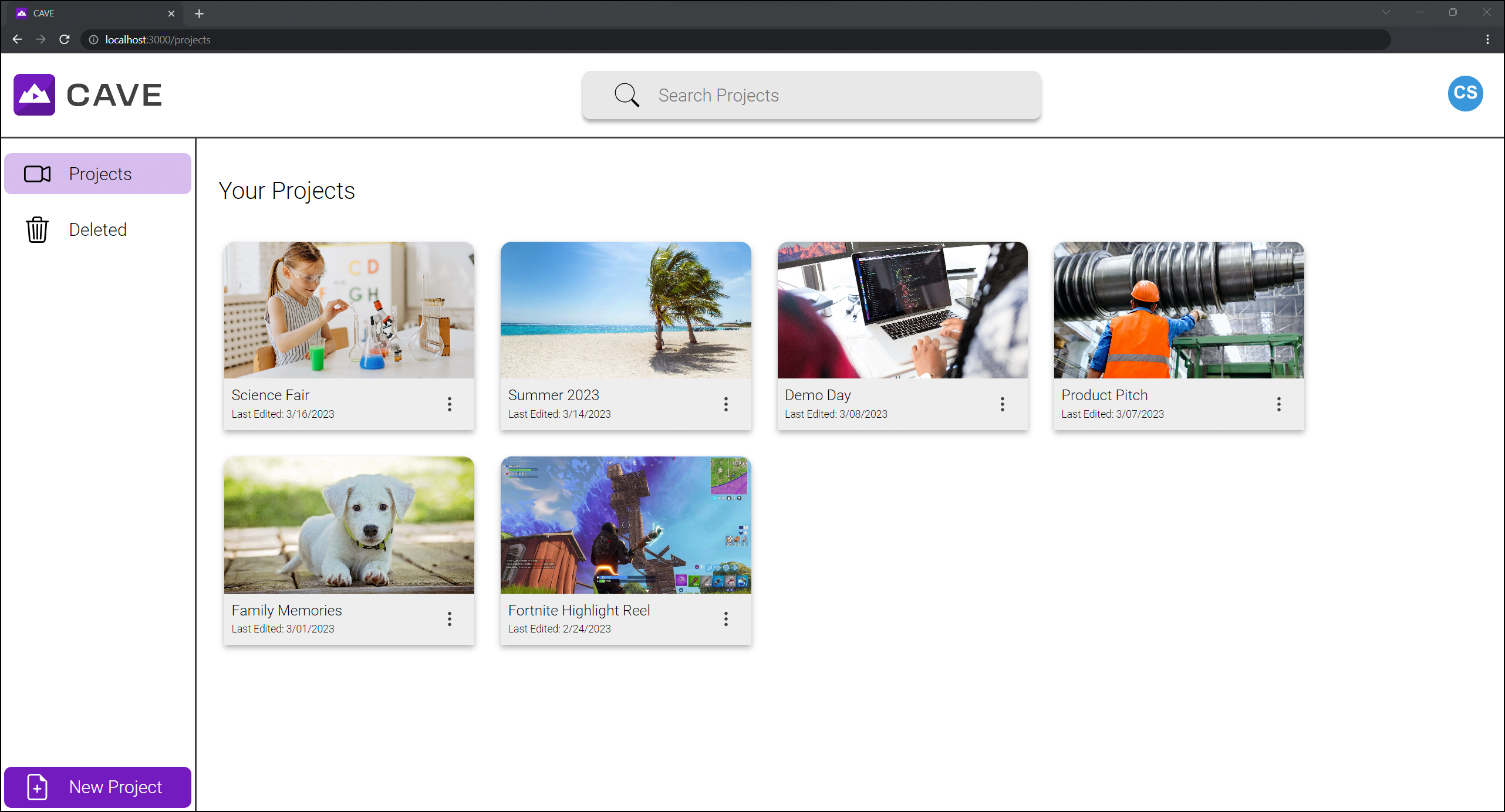
After logging in to the application, the user will land on the project management page, which displays all projects of which they are an owner or collaborator. Here the user may rename, delete, or filter through their projects. The ‘New Project’ button in the left pane allows the user to enter a name and resolution, and create a new project file.
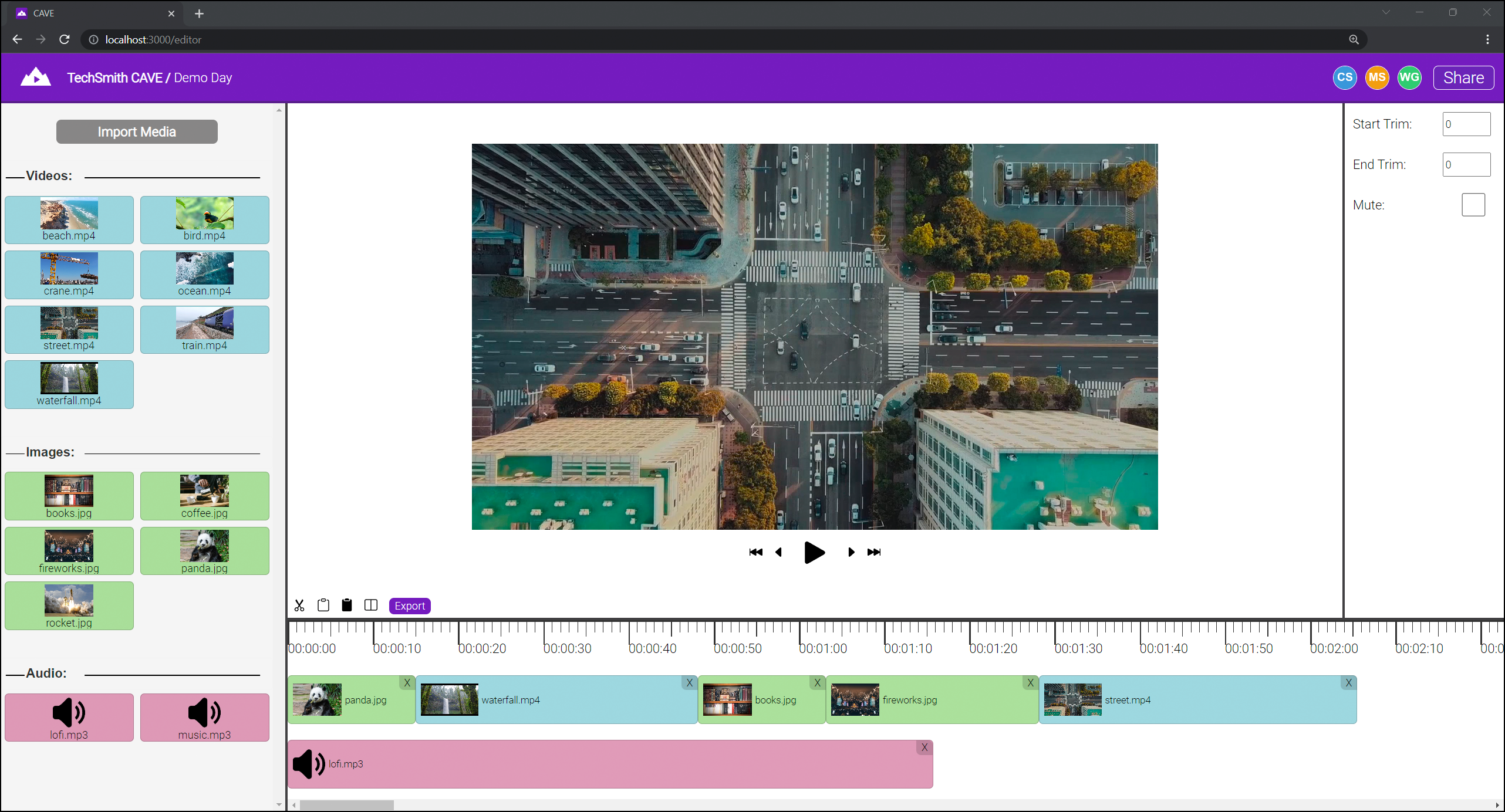
Upon opening a project, the user is taken to the video editor. The left pane of the editor contains the media bin, where the user can import video, image, and audio files into the project.
Media can be added to the project timeline at the bottom of the editor by dragging in blocks from the media bin. The timeline contains separate video and audio tracks, in which media blocks can be reordered, trimmed and duplicated. Changes made in the timeline are reflected in the preview that is automatically generated above.
The user can add collaborators to the project by opening the share modal (accessed from the top-right of the editor) and inviting others using the email associated with their account.
Once satisfied, a high-quality render of the final product can be downloaded to the user’s device by selecting the ‘Export’ button in the toolbar above the timeline.
For a thorough demonstration of some use cases for CAVE, please check out our Project Video! [software demo begins at 4:54]
My Role
In an effort to remain organized and establish a clear breakdown of responsibilities, our team decided to split into three subteams:
- Media processing, project serialization, and client synchronization: Wenrui Li, Craig Smith
- Front end (UI development): Marco Suriano, Kyle Wagner
- Server systems and authentication: Faran Meshinchi, Rachel Townson
We followed an Agile development model, ensuring timely completion of all deliverables and avoiding any deviation from the software specifications required by our client. Our team met once per week, at minimum, to work collaboratively and brainstorm ideas. We also had weekly meetings with each our client and project manager (a course TA) to showcase progress updates and discuss each member’s tasks for the following week.
My specific responsibilities included designing and implementing our SQL database and API endpoints, on which I collaborated with Rachel. Additionally, I integrated authentication with the Microsoft identity platform into our application; this allows users to sign into CAVE using their existing Microsoft account, and secures our API endpoints with granulized access control.
I also had the chance to do some work in React near the end of the development timeline as we shifted our focus to completing the front end.
Technologies and Architecture
Languages: JavaScript
Technologies: React, FFmpeg, Node.js, Microsoft Azure services
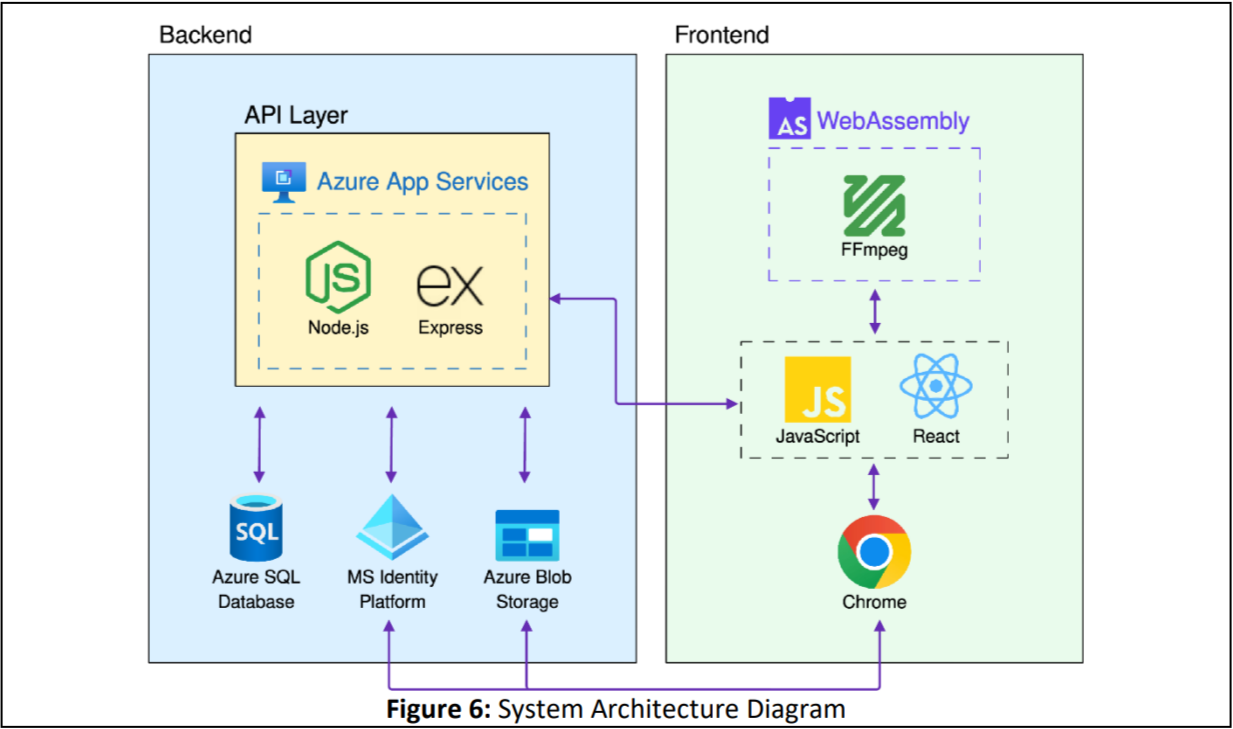
The CAVE web application is built on React and guarantees support for Chromium-based browsers. Video processing is accomplished client-side using FFmpeg, a powerful multimedia processing program.
The backend architecture is hosted on Microsoft Azure services. User authentication and authorization is handled by the Microsoft Identity Platform. Project state and user information is stored in Azure SQL database and shared media for each project is stored in Azure Blob Storage. The API is built on Express, a RESTful API framework for Node.js, and hosted on Azure App Service.
Access to the SQL database is mediated by the API endpoints. Clients can access Blob Storage resources directly, however, using access tokens issued through the API.
Awards
On Design Day, the conclusion of the capstone course, all teams showcase their software in a public expo which includes a panel of corporate judges. Our team was awarded the Amazon Sigma Award for the best overall capstone experience.